Analysis of Gmail Smart Compose: Real-Time Assisted Writing
-
date_range 29/10/2022 21:30 info
Here we introduce Gmail’s Smart Compose which provides real-time and interactive writing suggestions. It is a large-scale neural language mode of sequence prediction. We use the question-answer format here.
Q: What is the problem?
The problem is to improve Gmail user experience by assisting users in writing mails by reducing repetitive typing, gaining confidence in Gmail and improving user experience.
Q: How is it related to deep learning?
It predicts the next letter/words/phrases while a Gmail user is writing a sentence during an email writing process. This could be modeled to sequence prediction tasks for language models. With the development of machine and deep learning in NLP, the deep neural language model is more accurate but heavy-weight and computationally expensive. That brings to the industry-scale problem which Smart Compose is going to address.
Q: What is the mathematical modeling
It could be modelled as sequence to sequence prediction, which maximizes the log probability of producing the correct target sequence given the input for all data samples in the training corpus.
Q: What data and features are used?
Previous emails; subject of the e-mail; Date time and Locale of the user composing the e-mail. They perform preprocessing of the normalisation, tokenization; removing quotation, language detection etc. for the data. After the pre-processing steps, there are about 8 billion English messages in our data set. We split the data set into 80% for training and 20% for tests.
Q: How is the model selected?
These papers explores three types of deep neural language models with context-encoder or not, or a sequence2sequence attention model as shown in these figures below.
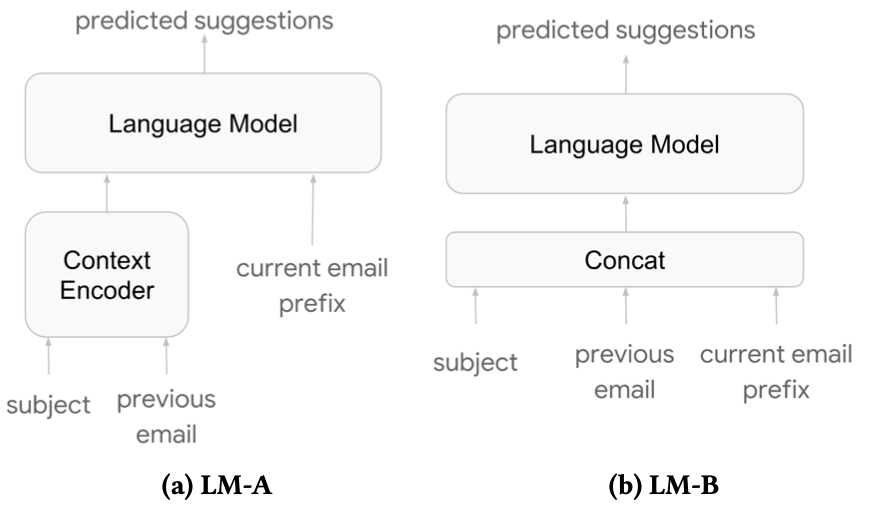
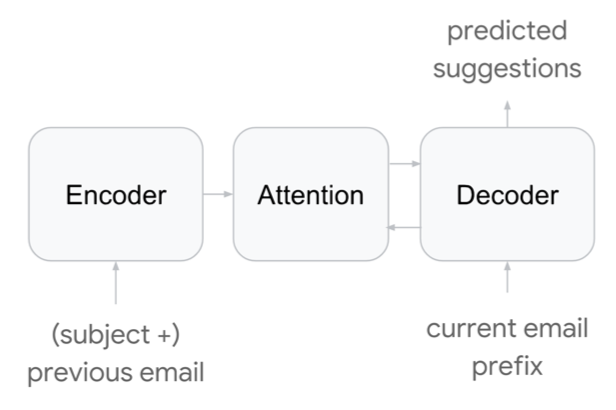
The first two models are modeled as the Language Model. It uses LSTM layers, with residual connections between consecutive layers. The third model is modelled as a sequence-to-sequence model with Transformer-based architecture. In all these approaches, the conditional inputs, including tokenized email content, categorical features such as date, time and locale, are fed to the language model through an embedding layer.
Q: How is the inference process?
In inference, they feed in necessary context fields (subject, previous email body, etc.) to the model and use a beam search procedure to generate n best suggestions The beam-search is using a heap of m best candidate. At each step, new token is generated and put in the heap to pick the top-k best token based on confidence score and add the k possible extensions into the heap. The confidence score is a length-normalized log conditional probability of each suggestion sequence More detail about beam search could be referenced: here . Each Smart Compose request is composed of a sequence of prefix encoding steps and beam-search steps. The Smart Compose is implemented within a streaming RPC server. The APP logic in a high-level service decides the running of Smart Compose for a message.
Q: What is the performance evaluation?
Two metrics are used. Log Perplexity (similar to information entropy) and ExactMatch@N (the percentage of predicted phrases that exactly matches the first N words in the ground truth text, where N=15 here).
Q: What is the baseline used?
The baseline model here used is the LSTM language model of 2 layers with 1024 hidden units for each layer without any context embeddings from subject or previous e-mail.
Q: which model is selected for trade-off of moddel quality and inference latency?
LM-A is chosen to be the most production-appropriate model taking into account strict production latency constraint and very high request volume. The third model based on Transformer has the highest quality, but quality gap between the the first two model and Transformer based model is less evident in the ExactMatch metric than in the log perplexity metric, and the ExactMatch metric is more important to production.
Q: How to make a personalized recommendation?
It develops a global model and personalized model. Then it assigns different weights on the personalized model and the global model as the final sequence prediction to achieve the personzlied recommendation?
The personalzied model is a light-weight language model adapted to the user’s personal mail data.
Q: What is my opinion for Smart Compose?
It has been shown to have given some helpful predictions in some cases when I was using it. However, the response is still not accurate enough or the prediction is not coming up when I really need it. Also it seems to have some gender-bias or other privacy problem that needs to be addressed.
Reference:
Chen, M.X., Lee, B.N., Bansal, G., Cao, Y., Zhang, S., Lu, J., Tsay, J., Wang, Y., Dai, A.M., Chen, Z. and Sohn, T., 2019, July. Gmail smart compose: Real-time assisted writing. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining (pp. 2287-2295).
